Imran Hussain says, Biomass is burnt during cooking, waste disposal, cremation activities etc. Cremation alone accounts considerably to air pollution
Fake news claim: A message viral on social media claiming “Cremation alone accounts considerably to air pollution. Across India, each year a huge quantity of wood is used in cremation.”
Examples of viral posts in circulation on Social Media like WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, etc.
Burning of biomass such as wood, leaves, manure etc has been identified as one of the most significant contributors to air pollution in Delhi. Biomass is burnt during cooking, waste disposal, cremation activities, etc. Cremation alone accounts considerably to air pollution. Across India, each year a huge quantity of wood is used in cremation.
Facts Check Verdict: True
News Verification: The message was given by Delhi AAP government, Environment Minister Imran Hussain. It is a true message made by the app minister and also available on the AAP website.
In a letter written to Union Environment Minister Anil Madhav Dave, he said that there is an urgent need to convert existing wood based crematoria into green crematoria as burning of biomass such as woods, manure among others are the most significant contributors to air pollution in Delhi. “I therefore request the Central government to consider constituting a technical committee for drafting a model policy for creating a standardized design for the green crematoria,” he said, adding that cremation alone accounts considerably to air pollution and across India, each year huge quantity of wood is used in cremations.
The above information is a huge sentiment to Hindus across the world.
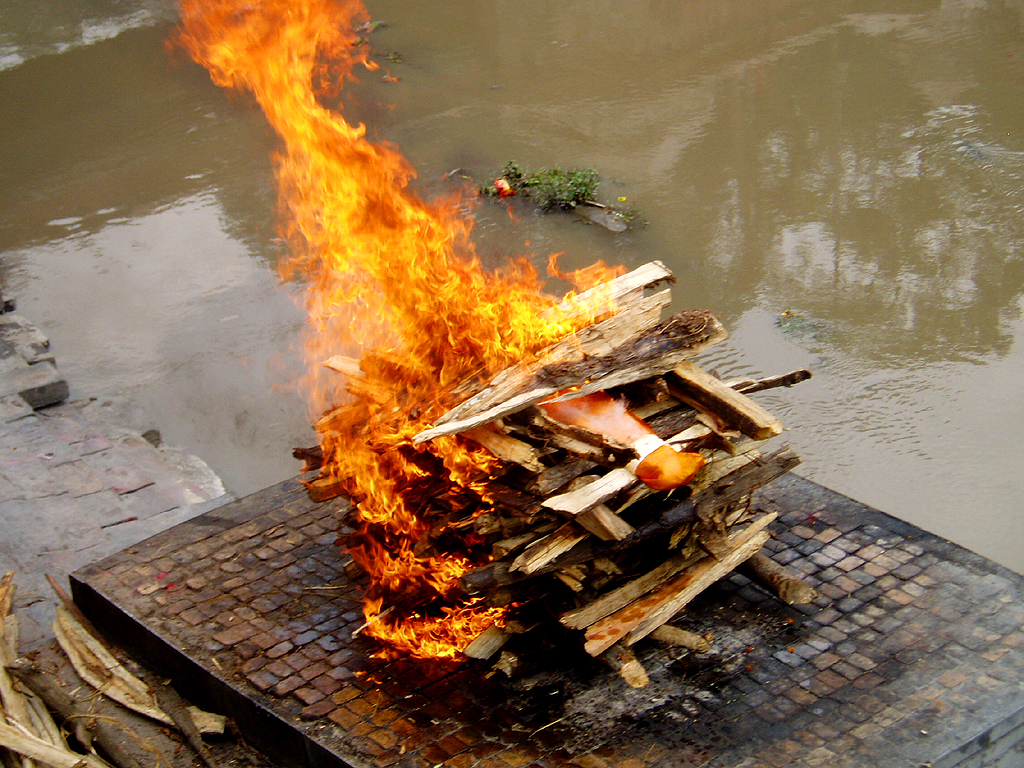

In 2016, The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has questioned the centuries-old tradition practiced by Hindus to cremate dead bodies at the river banks, saying the method of burning wood leads to air pollution
The green panel said the traditional means of cremation caused an adverse impact on the environment and dispersal of ashes in the river led to water pollution.
"Religions of the world, therefore, conceived of different methods for disposal of the dead on the basis of their theology and the circumstances in which the believers lived. Where there was plenty of wood, the individuals thought of disposal of their dead by burning with wood, but where there was a scarcity of wood the individuals buried their dead," it said.
In Hinduism, the cremation ground (shmashana ghat) is located near a river, if not on the river bank itself. According to tradition, a dead body is washed by family members in the river water before being put on the wood pyre with feet facing south. It is said that Hindus believe that the soul of a dead person must be completely detached from the body to attain 'moksha'. And for this, an open cremation is needed so that the soul can be released easily as soon as the body is set on fire. The ashes are later immersed in the river completing the rite.
The NGT was hearing a plea by advocate DM Bhalla who had said that cremation of humans by conventional methods added to air pollution, therefore, alternative modes of cremation needed to be used.
As per CNN, Fifty to 60 million trees are burned during cremations every year in India, according to Moksha, a Delhi-based NGO working to reduce the environmental impact of funeral pyres.
Air pollution and deforestation are not the only environmental threats caused by cremation: They also generate large quantities of ash, which are later thrown into rivers, adding to the toxicity of their waters, according to Moksha.
As per the US National Library of Medicine, The process of corpse cremation generates numerous harmful air pollutants, including particulate matter (PM), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and heavy metals. These pollutants could have severe effects on the surrounding environment and human health. Currently, the awareness of the emission levels of harmful air pollutants from cremators and their emission characteristics is insufficient. In this study, we obtained the emission characteristics of flue gas from cremators in Beijing and determined the localized emission factors and emission levels of harmful air pollutants based on actual monitoring data from nine typical cremators. The results show that the emissions of air pollutants from the cremators that directly discharge flue gas exceed the emission standards of China and Beijing.