The Air We Breathe: Unveiling the Composition of Earth's Atmosphere
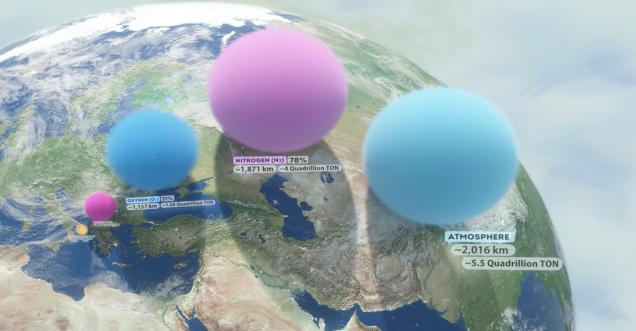
The Earth's atmosphere comprises various gases, the most abundant ones being nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2). Here's an approximate breakdown of the major components of Earth's atmosphere by volume:
-
Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, making up about 78% of the total volume.
-
Oxygen (O2): Oxygen is the second most abundant gas, accounting for roughly 21% of the atmosphere's volume.
-
Argon (Ar): Argon is the third most common gas, constituting approximately 0.93% of the atmosphere.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Carbon dioxide makes up a relatively small but essential portion of the atmosphere, typically around 0.04% to 0.041% by volume. Its concentration has been increasing due to human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels.
-
Neon (Ne), Helium (He), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe): These noble gases are present in trace amounts, collectively making up less than 0.001% of the atmosphere.
-
Water Vapor (H2O): The amount of water vapour in the atmosphere varies significantly with location and weather conditions, typically ranging from 0.1% to 4% in the lower atmosphere. Water vapour plays a crucial role in weather and climate.
-
Trace Gases: There are various other trace gases in the atmosphere, including methane (CH4), ozone (O3), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and others. These gases are in minimal concentrations, typically less than 0.001%.
It's important to note that the composition of Earth's atmosphere can vary slightly depending on factors such as altitude, location, and climate. The figures represent average sea-level concentrations in the lower atmosphere (troposphere).
























